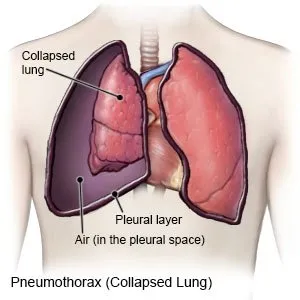
Pneumothorax; The meaning of the word is that there is air in the chest cavity, where it should not be. This air accumulates in the rib cage outside the lungs. The result is that the lungs are extinguishing, ie collapse and find the patient as a respiratory distress. Causally, spontaneous and secondary pneumothorax (PX) are divided into two. Spontaneous PX is the explosion of bubbles called bullacies in the lungs as a result of the explosion of the air in the lungs to the pleural cavity. It is common in weak tall young men.
Secondary PX is the main title; It occurs as a result of the underlying parenchyan disease or trauma. Parenchy disease varies depending on age. Lung immaturity in the newborn age group (hyaline membrane, surfactant failure) may cause tear in the paran about positive pressure ventilation. In older children, infectious conditions such as pneumonia and ampiyem are seen as factor. As the age grows, the trauma becomes more prominent.
As a result of trauma, PX is most commonly caused by the ribs of the ribs into the pleura. The air in the lung, the bronchial system, escapes to the pleural cavity. In the open injuries of the thoracic, the air enters the chest cavity from the outside, which in this case the air cannot be exhausts and gradually starts to accumulate more and more air. This condition, called blood pressure px, is increasingly life -threatening. A more severe picture is seen as a result of the contusion of the thoracic, which is seen here, where both PX and the lung parenchyma have blood and interstitial fluid escape into the alveolar area. This causes oxygen exchange to deteriorate the lung, which is not available due to both parenchymal damage and PX. It is also a serious condition to have laceration in the main airways, trachea and main bronchi. In the event that the epiglot is closed, trachea and main bronchi may be injured in traumas to the direct neck area. Subcontracting ampisemia is typically available here. The emphysema increases in every inspirium.
The patient's felt is not enough breathing, that is, dyspnea. Chest pain, rapid breathing, tachycardia are other findings. An unexpected decrease in blood oxygen saturation is seen in intubated patients. Respiratory sounds cannot be taken or decreased on the side of PX. Typical appearance on lung radiography; The lung is collabes and the presence of air in the chest cavity. Since it is expected in secondary PXs, it is diagnosed with the same appearance in graphic controls, even if not symptomatic. Lung tomography can be taken in suspicious cases or for differential diagnosis.
The gold standard tube in treatment is thoracostomy and underwater drainage. The patient is taken from the intercostal range in the 3rd to 5th intercostal range. When the pleura is passed, the sound of the air is heard. Tube detection and underwater drainage are taken, the PX is thrown from the bottle. Control lung graph is taken and the location of the tube is seen. The duration of the tube in the clinical condition of the patient varies. The negative pressure applied to the bottle while the tube is pulled and the pleura is adhered to the chest wall. Recurrent PXs have an indication of thoracoscopy.
The page content is only for informational purposes, you should consult your doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
Comments